Refractive error - Hypermetropia
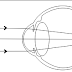
Defination: hypermetropia (hyperopia) 0r long sightedness is the refravtive stste of eye wherein the parallel rays of light coming from infinity are focused behind thr retina with accommodation bieng at rest.
 |
| fig: Hypermetropia |
Etiology
- Axial hypermetropia: In this the total power of eyeball is normal but there is axial shortening of eyeball. 1 mm shortening results in 3D of hypermetropia
- curvatural hyermetropia is the comdition in which the curvature of cornea lens or both is flatter than normal( decrease in curveness) reaults indecrease in the refractive power of the eye.
- Index hypermetropia occurs due to decrease in refractive index of the lens in old age. It may also occur in diabetics under treatment.
- Positional hypermetropia results from posteriorly placed crystalline lens.
- Absence of crystalline lens either congenitally or acquired (following surgical removal or posterior dislocation) leads to aphakia — a condition of high hypermetropia.
clinical types
There are three clinical types of hypermetropia:
1. Simple or developmental hypermetropia is the commonest form. It results from normal biological variations in the development of eyeball. It includes axial and curvatural hypermetropia.
2. Pathological hypermetropia results due to either congenital or acquired conditions of the eyeball which are outside the normal biological variations of the development. It includes :
Index hypermetropia (due to acquired cortical sclerosis),
Positional hypermetropia (due to posterior subluxation of lens),
Aphakia (congenital or acquired absence of lens) and
Consecutive hypermetropia (due to surgically over-corrected myopia).
3. Functional hypermetropia results from paralysis of accommodation as seen in patients with third nerve paralysis and internal ophthalmoplegia.
Nomenclature (componentsof hypermetropia)
Nomenclature for various components of the hypermetropia is as follows:Total hypermetropia is the total amount of refractive error, which is estimated after complete cycloplegia with atropine. It consists of latent and manifest hypermetropia.
1. Latent hypermetropia implies the amount of hypermetropia (about 1D) which is normally corrected by the inherent tone of ciliary muscle. The degree of latent hypermetropia is high in children and gradually decreases with age. The latent hypermetropia is disclosed when refraction is carried after abolishing the tone with atropine.
2. Manifest hypermetropia is the remaining portion of total hypermetropia, which is not corrected by the ciliary tone. It consists of two components, the facultative and the absolute hypermetropia.
i.Facultative hypermetropia constitutes that part which can be corrected by the patient's accommodative effort.
ii. Absolute hypermetropia is the residual part of manifest hypermetropia which cannot be corrected by the patient's accommodative efforts.
Thus, briefly: Total hypermetropia = latent + manifest (facultative + absolute).
Hypermetropia notes
 Reviewed by Guffy
on
November 07, 2019
Rating:
Reviewed by Guffy
on
November 07, 2019
Rating:
 Reviewed by Guffy
on
November 07, 2019
Rating:
Reviewed by Guffy
on
November 07, 2019
Rating:










No comments: